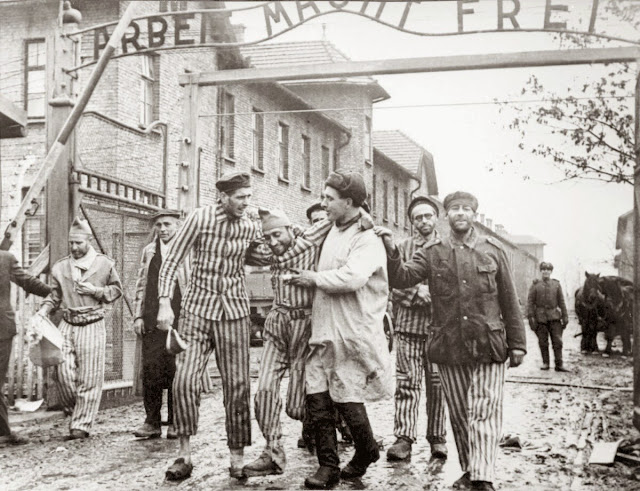
Red Army Liberation of Auschwitz I, January 27th 1945.
In reality, the liberation of Auschwitz, Auschwitz-Birkinau and Auschwitz-Monowitz was largely symbolic, since the SS had evacuated much of the camp populace in a series of Death Marches anticipation of the Soviet advance, meaning that the camps themselves were largely abandoned, with only a few dozens or perhaps hundred of inmates remaining there, unguarded and unsupervised when the Red Army arrived to "liberate" them.
But the point is, the camp was liberated by the Red Army - and most of them were Russians.
In reality, the liberation of Auschwitz, Auschwitz-Birkinau and Auschwitz-Monowitz was largely symbolic, since the SS had evacuated much of the camp populace in a series of Death Marches anticipation of the Soviet advance, meaning that the camps themselves were largely abandoned, with only a few dozens or perhaps hundred of inmates remaining there, unguarded and unsupervised when the Red Army arrived to "liberate" them.
But the point is, the camp was liberated by the Red Army - and most of them were Russians.
- "Prime Minister" Arseniy Yatsenyuk,
NATO Proconsul of Nulandistan
"Russia, like most invited nations, is sending a lower-ranked official and will be represented by the Kremlin's chief of staff, Sergei Ivanov.
This unusual diplomacy deteriorated into a public spat when a Polish radio station asked the country's foreign minister, Grzegorz Schetyna whether it was petty not to invite Mr Putin.
He decided to answer by crediting the Ukrainians for liberating Auschwitz, rather than the Soviet Union's Red Army.
'Anti-Russia hysteria'
Moscow was incensed, saying it was time to stop "ridiculing history" and engaging in "anti-Russia hysteria". Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov said Mr Schetyna's comments were "blasphemous and cynical".
He pointed out Auschwitz was liberated by a Red Army consisting of Russians, Ukrainians, Chechens, Georgians and Tatars.
Auschwitz was liberated by the Red Army's First Ukrainian Front, which certainly included both Ukrainians and Russians. Maj Anatoly Shapiro, a Ukrainian Jew, led the battalion that fought its way into the camp.
On Friday Mr Schetyna insisted he was right because, as he said, it was "obvious" that a multi-ethnic Red Army liberated Auschwitz, but it had in fact been a Ukrainian officer, Igor Pobirchenko, whose tank was the first to break through the camp's gates.
Civic Leaders of Kiev welcome the German Occupiers, August 1941
"All Yids[a] of the city of Kiev and its vicinity must appear on Monday, September 29, by 8 o'clock in the morning at the corner of Mel'nikova and Doktorivska streets (near the cemetery).
Bring documents, money and valuables, and also warm clothing, linen, etc.
Any Yids[a] who do not follow this order and are found elsewhere will be shot.
Any civilians who enter the dwellings left by Yids[a] and appropriate the things in them will be shot."
—Order posted in Kiev in Russian by the Bandera Nazis,
on or around September 26, 1941.
Through their virtual disinvitation, EU countries are preventing the Russian president from participating at the commemoration of the 70th anniversary of the liberation of Auschwitz. The highest representative of the country, whose army had halted the mass murder in the German extermination camp January 27, 1945, is thereby excluded from the commemoration ceremonies. However, Germany’s president, will participate. Joachim Gauck had already used his speech on the 75th anniversary of Germany’s invasion of Poland, to massively stir up sentiments against Moscow and to transform the commemoration of Nazi crimes into an appeal for closing ranks against Russia. In his memoirs, Gauck described Red Army soldiers, who had liberated Germany, as beings “with Asian facial features,” “reeking of Vodka,” who “requisitioned and stole.” A few years ago, he complained, “the occurrence of the German Judeocide has been inflated to a uniqueness,” because “certain milieus of post religious societies” were seeking “a certain shudder in face of the unspeakable.” In 2010, he was quoted saying, he “wonders how much longer we Germans want to nurture our culture of chagrin.”
“Just Like Nazi Troops”
The commemoration of the 70th anniversary of the liberation of the German Auschwitz extermination camp had been the focus of political intrigues already last year. At the commemoration of the 60th anniversary of its liberation, Russian President Vladimir Putin’s participation was still taken for granted. After having suffered severe losses, the Soviet Army reached Auschwitz January 27, 1945, putting an end to the ghastly murders Germans were committing.
First attempts to exclude Putin from the commemoration of the 70th Anniversary were made in Poland in the summer 2014. A parliamentarian was quoted saying that the Red Army “had been an aggressor” in WW II, “just like Nazi troops,” which is why the Russian President should only be allowed to make a “penitential pilgrimage” to Poland.[1] At the time, Bronisław Komorowski could see nothing wrong with Putin’s participation at the Auschwitz commemoration. However, anti-Russian forces have prevailed and the Russian President’s invitation was cancelled through diplomatic channels. According to reports, Poland’s Prime Minister Ewa Kopacz has also campaigned to prevent Putin from participating at a parallel commemoration ceremony in Prague. This would exclude the president of the country, whose army had lost more than a million soldiers just to liberate the German Reich and the Polish territories under German occupation.
Turned against Russia
The anti-Russian instrumentalization of the memory of German crimes against humanity is making headway with Putin’s virtual disinvitation. Already on September 1, 2014, German President Joachim Gauck used his memorial address in Gdansk — commemorating the 75th Anniversary of the German invasion of Poland — to stir up anti-Russian sentiments. Referring to the Ukraine conflict, Gauck accused Russia of giving a higher priority to “a quest for power,” rather than to “maintaining stability and peace.” Completely blotting out western support for the Ukrainian putsch and the civil war, while ignoring all the wars waged by the West from Yugoslavia to Iraq on up to Libya, Gauck alleged that Russia had “violated international law” and “annexed foreign territory.“[2] Alluding to Great Britain and France’s approbation for Germany’s occupation of parts of Czechoslovakia in October 1938, targeting Russia, Gauck declared, “history teaches us that territorial concessions often whet the appetite of the aggressors.” The commemoration of Nazi crimes was thereby transformed into an appeal to close ranks against Russia, which Germany had invaded.
A “Culture of Chagrin”
On various occasions before becoming president, Gauck, who, unlike Russia’s President Putin, will be present at Auschwitz January 27, had made public statements showing how he views Germany’s 1945 liberation and the Shoah. In his memoires, he wrote on the subject of Germany’s liberation, that it arrived as “horrible news,” he depicted the Red Army soldiers as beings “with Asian facial features,” reeking “of vodka,” who “requisitioned and stole” and systematically raped women.[3] 2006, Gauck remorsefully claimed that there is “a tendency toward sanctifying the Holocaust,” wherein “the occurrence of German Judeocide is inflated to a uniqueness that ultimately escapes comprehension and analysis.” “Certain milieus of post-religious societies” were persistently searching “for the dimension of the absolute, a certain shudder in face of the unspeakable.” This could also be achieved by “the absolute evil” and is “paradoxically of psychological advantage.“[4] Gauck has stated several times that “the Germans” would be well advised to change their approach to history. In the fall of 2010, he mused, “I ask myself, how much longer do we Germans want to nurture our culture of chagrin.“[5] This was after he had positively responded to the question whether “the majority of the Germans” are mature enough for a “reorientation toward their own victims, the reorientation toward the patriotic.” “That’s how I see it.“[6]
Broad Brush
Until he was inaugurated president, Gauck’s historical views were criticized in German public opinion, For example, he has a knack for using the “broad brush,” in reference to his remarks on the “Black Book of Communism.“[7] Gauck had written that “the communists had also made themselves unpopular, when they ... approved Poland’s westward acquisition of territory and thereby Germany’s loss of its eastern territories.” “To both the natives and the expellees, this loss of the homeland was considered a great injustice, which the communists sealed in 1950, by recognizing the Oder-Neisse as the new German-Polish border,“[8] alleges Gauck. In the conflict over the “Centre against Expulsions,” he took the side of the president at the time, Erika Steinbach, who was sharply criticized for her historical revisionist statements, particularly in Poland. Gauck is quoted on the German League of Expellees’ (BdV) website saying, Berlin is most certainly the best location for a “Centre against Expulsions.” It blends in, because Berlin is where “there are various ‘topographies of terror,’ the location of the Wannsee Conference and the Stasi Headquarters, the former seat of government of brown and red despots.“[9]
Yatsenyuk’s “Soviet Invasion”
Gauck’s Auschwitz speech and Putin’s disinvitation coincide with Berlin’s open cooperation with the fascist successors of Nazi collaborators to stage a pro-western coup in Kiev. (german-foreign-policy.com reported.[10]) The Kiev government has adopted their anti-Russian standpoints, which are also increasingly having an influence on the German debate where they dovetail with old anti-Russian sentiments. Arseniy Yatsenyuk recently caused a stir with his interview on German television. He literally alleged, “We all remember well the Soviet invasion of Ukraine and Germany.“[11] This statement has remained unchallenged.
[1] Streit in Polen über Einladung Putins zu Auschwitz-Gedenken 2015. www.tt.com 09.05.2014.
[2] Gedenkfeier zum deutschen Überfall auf Polen 1939. www.bundespraesident.de 01.09.2014.
[3] Joachim Gauck: Winter im Sommer, Frühling im Herbst. München 2009. See Hans-Rüdiger Minow: Der Zug der Erinnerung, die Deutsche Bahn und der Kampf gegen das Vergessen.
[4] Joachim Gauck: Welche Erinnerungen braucht Europa? www.robert-bosch-stiftung.de. See The Consensus President.
[5] “Mutige Politiker ziehe ich vor”. www.sueddeutsche.de 30.09.2010.
[6] Gauck: Erinnerung an Vertreibung leugnet nicht den Nazi-Terror. www.dradio.de 31.08.2006.
[7] Daniela Dahn: Gespalten statt versöhnt. www.sueddeutsche.de 10.06.2010.
[8] Stéphane Courtois et al.: Das Schwarzbuch des Kommunismus. Unterdrückung, Verbrechen und Terror. München 1998.
[9] www.z-g-v.de.
[10] See Vom Stigma befreit